
Some languages, however, provide features that separate interface and implementation.

There is a distinction between the definition of an interface and the implementation of that interface however, this line is blurred in many programming languages because class declarations both define and implement an interface.
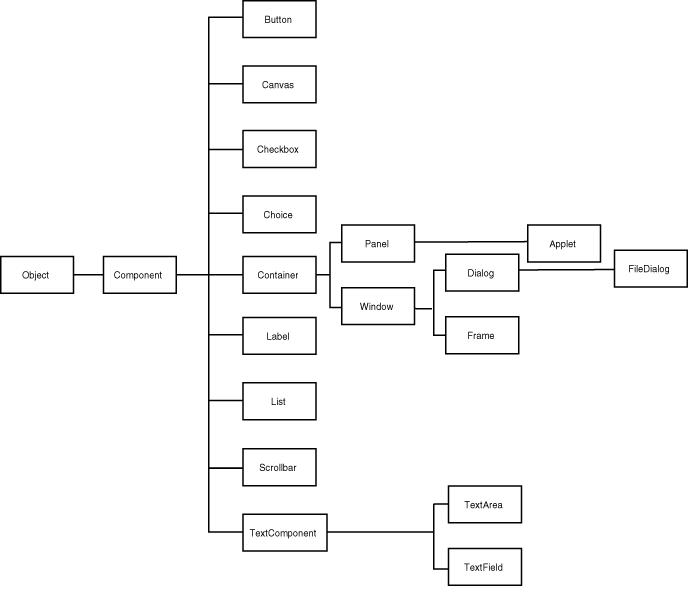
The class at the top of the awt hierarchy is code#
Structure consists of data and state, and behavior consists of code that specifies how methods are implemented. Programming languages that include classes as a programming construct offer support, for various class-related features, and the syntax required to use these features varies greatly from one programming language to another.Įvery class implements (or realizes) an interface by providing structure and behavior. Often only a single implementation of a type is given, in which case the class name is often identical with the type name.Ĭlasses are composed from structural and behavioral constituents. The ABCBanana class could then produce particular bananas: instances of the ABCBanana class would be objects of type Banana. For example, a Banana type might represent the properties and functionality of bananas in general, while the ABCBanana and XYZBanana classes would represent ways of producing bananas (say, banana suppliers or data structures and functions to represent and draw bananas in a video game).
Similarly, a given class may have several different constructors.Ĭlass types generally represent nouns, such as a person, place or thing, or something nominalized, and a class represents an implementation of these. Different (concrete) classes can produce objects of the same (abstract) type (depending on type system) for example, the type Stack might be implemented with two classes – SmallStack (fast for small stacks, but scales poorly) and ScalableStack (scales well but high overhead for small stacks). In the terms of type theory, a class is an implementation-a concrete data structure and collection of subroutines-while a type is an interface. At the same time, a class has an implementation (specifically the implementation of the methods), and can create objects of a given type, with a given implementation. In its most casual usage, people often refer to the "class" of an object, but narrowly speaking objects have type: the interface, namely the types of member variables, the signatures of member functions (methods), and properties these satisfy. 3.3 Orthogonality of the class concept and inheritance.In these languages, a class that creates classes within itself is called a metaclass. In certain languages, classes are, as a matter of fact, only a compile-time feature (new classes cannot be declared at run-time), while in other languages classes are first-class citizens, and are generally themselves objects (typically of type Class or similar). When an object is created by a constructor of the class, the resulting object is called an instance of the class, and the member variables specific to the object are called instance variables, to contrast with the class variables shared across the class. the real world, machine learning, AI) more easily. Thus they can model dynamic systems (i.e.

Although, to the point of conflation, one could argue that is a feature inherent in a language because of its polymorphic nature and why these languages are so powerful, dynamic and adaptable for use compared to languages without polymorphism present. In many languages, the class name is used as the name for the class (the template itself), the name for the default constructor of the class (a subroutine that creates objects), and as the type of objects generated by instantiating the class these distinct concepts are easily conflated. In object-oriented programming, a class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, providing initial values for state ( member variables) and implementations of behavior (member functions or methods).

Definition in programming that specifies how an object works


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
